Affiliate Disclaimer:
FishKeepingAnswers.com is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site we may earn a commission.
The Leopard Bush Fish, which is also sometimes called the Leopard Climbing Bush Fish, is a truly stunning fish that originates from Central Africa. These fish are hardy, colorful, and look stunning in a well-planted aquarium. The Leopard Bush Fish is a great gateway fish to the world of ‘oddball’ fish keeping.
I have been keeping Leopard Bush Fish for around 5 years now. They are amazing fish that are incredibly hardy. They grow slowly but are generally long-lived. I keep mine in a ‘community’ of other similar-sized ‘oddball’ fish.
Characteristics
| Common Name: | Leopard Bush Fish |
| Scientific Name: | Ctenopoma acutirostre |
| Family: | Anabantidae |
| Origin: | The central African Republic and Democratic Republic Congo |
| Tank Distribution: | Mid-water |
| Adult Size: | 8” (20cm) |
| Life Expectancy: | 15+ years |
| Care Level: | Intermediate |
| Minimum Tank Size: | 120 gallons (540 Litres) |
| Breeding Method: | Surface spawner |
| Temperature: | 70°F – 82°F (20°C – 28°C) |
| pH: | 5.5 – 7.5 |
| Hardness: | 35 – 210 ppm |
Leopard Bush Fish Origins
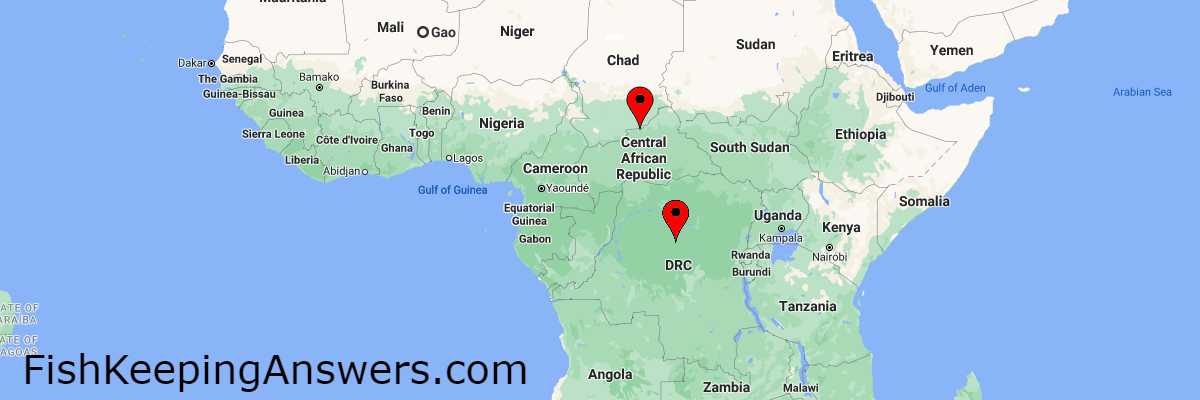
The Leopard Bush Fish originates from rivers and streams in both the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of Congo, both of which are located in the heart of central Africa.
Leopard Bush Fish Habitat
Leopard Bush Fish are found in waterways that cover a vast area of central Africa. They have adapted to be able to survive in environments ranging all the way from highly oxygenated, fast-flowing streams to pools which would be described as ‘stagnant’.
What Size Aquarium For Leopard Bush Fish?
Leopard Bush Fish require a decent-sized aquarium with some open swimming space but also some cover and hiding places.
I currently keep my Leopard Bush Fish in a 155 gallon (600 liters) aquarium which measures around 5’ (160cm) long. I have set their aquarium up with lots of plant growth, including a mat of floating water lettuce.
I have a fair few pieces of aquarium wood. These fish really appreciate a well-planted aquarium.
Leopard Bush Fish prefer a dimly lit aquarium, so a low-power light fitting is ideal. Adding floating vegetation helps reduce the light levels further.
These hardy and adaptable fish have evolved to live in a wide variety of environments, and as such don’t mind high or low flow, but they do like their water clean, so good filtration is important. I currently filter my Leopard Bush Fish aquarium using a Fluval FX4 (more on Fluval filters in this article I wrote titled Are Fluval Filters Good?).
Leopard Bush Fish Behavior In The Aquarium
Leopard Bush Fish are predators. They will eat smaller fish, so careful consideration should be given to tank mates. An adult Leopard Bush Fish will eat other fish up to around the size of a female guppy.
Leopard Bush Fish work well in a community of similar-sized fish, although they don’t work well with aggressive fish, like larger African Cichlids. I keep my Leopard Bush Fish with a school of Silver Dollars and a couple of Plecos.
What Do Leopard Bush Fish Eat?
These fish are carnivores through and through. They prefer meaty foods, although some aquarists report their Leopard Bush Fish will accept dry foods. My Leopard Bush Fish have never really taken to dried foods. I feed mine small prawns, pieces of fish meat, and earthworms (which I sometimes have to chop up a little).
Young, small Leopard Bush Fish can be fed frozen bloodworms, daphnia, and mosquito larvae.
Although the Leopard Bush Fish is a predator, feeder goldfish should be avoided as they offer little in the way of nutrients and often are a source of pests and diseases that can be introduced into your aquarium.
Breeding Leopard Bush Fish In Captivity
Like so many members of the Anabantidae family, Leopard Bush Fish lay their eggs on the surface of the aquarium water. They prefer to lay their eggs amongst floating vegetation.
When spawning, Leopard Bush Fish embrace near the surface. During the embrace, eggs and sperm are released simultaneously and the fertilized eggs float to the surface to rest in the floating vegetation. The parents take no part in guarding or raising the fry. The eggs take around 48 hours to hatch and the fry become free-swimming after 2 days.
Although there are few reports of Leopard Bush Fish successfully spawning in captivity, the reports I could find suggest Leopard Bush Fish need to ‘pair off’ voluntarily.
It is suggested that, if an aquarist hopes to breed leopard Bush Fish in captivity, they should start by sourcing a group of young Leopard Bush Fish and raising them as a group, increasing the chances of a successful pairing.
In Conclusion
If you are considering keeping some Leopard Bush Fish, I can highly recommend them. Keep one or more in a well-planted community tank with a group of similar-sized fish and you won’t regret it.
Leopard Bush Fish are hardy, long-lived, and make a great addition to any collection.







